Actinic Purpura
FEATURED VIDEOS
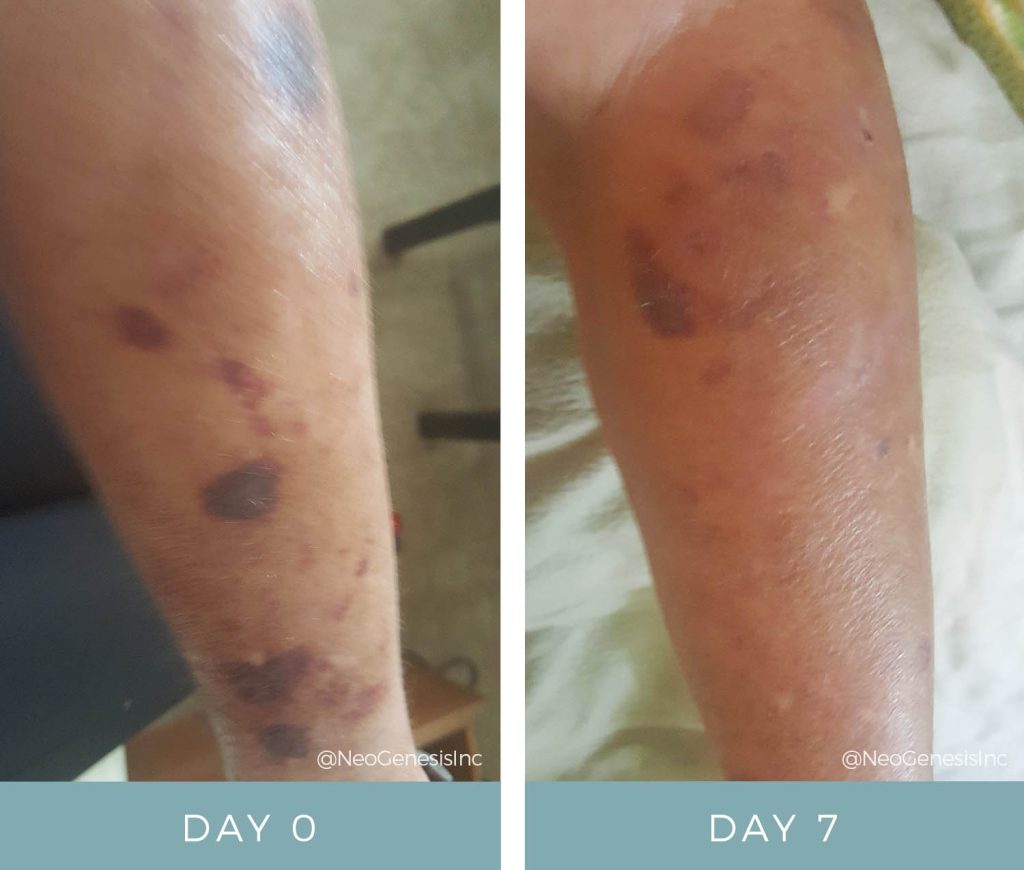
ACTINIC PURPURA
Actinic purpura, also known as solar purpura or senile purpura, is a skin condition that primarily affects older adults. It is characterized by the appearance of purple or red bruises on the arms, hands, and face. These bruises are caused by damage to the blood vessels in the skin due to long-term sun exposure.
The term “actinic” refers to the ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun that cause the skin damage. As we age, our skin becomes thinner and less elastic, making it more susceptible to bruising. In addition, prolonged exposure to UV rays can weaken blood vessel walls, leading to easy bruising.
Actinic purpura is a benign condition and does not pose any serious health risks. The bruises may take weeks to fade away, leaving behind a yellowish or brownish discoloration that can last even longer.
While actinic purpura is more common in older individuals, it can also affect younger people who have had significant sun exposure throughout their lives. People with fair skin and those who live in sunny climates are at a higher risk of developing this condition.
There is no specific treatment for actinic purpura, but there are steps that can be taken to minimize its appearance. These include wearing protective clothing and sunscreen when spending time outdoors, avoiding prolonged sun exposure during peak hours, and using moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and less prone to bruising.
FEATURED VIDEOS
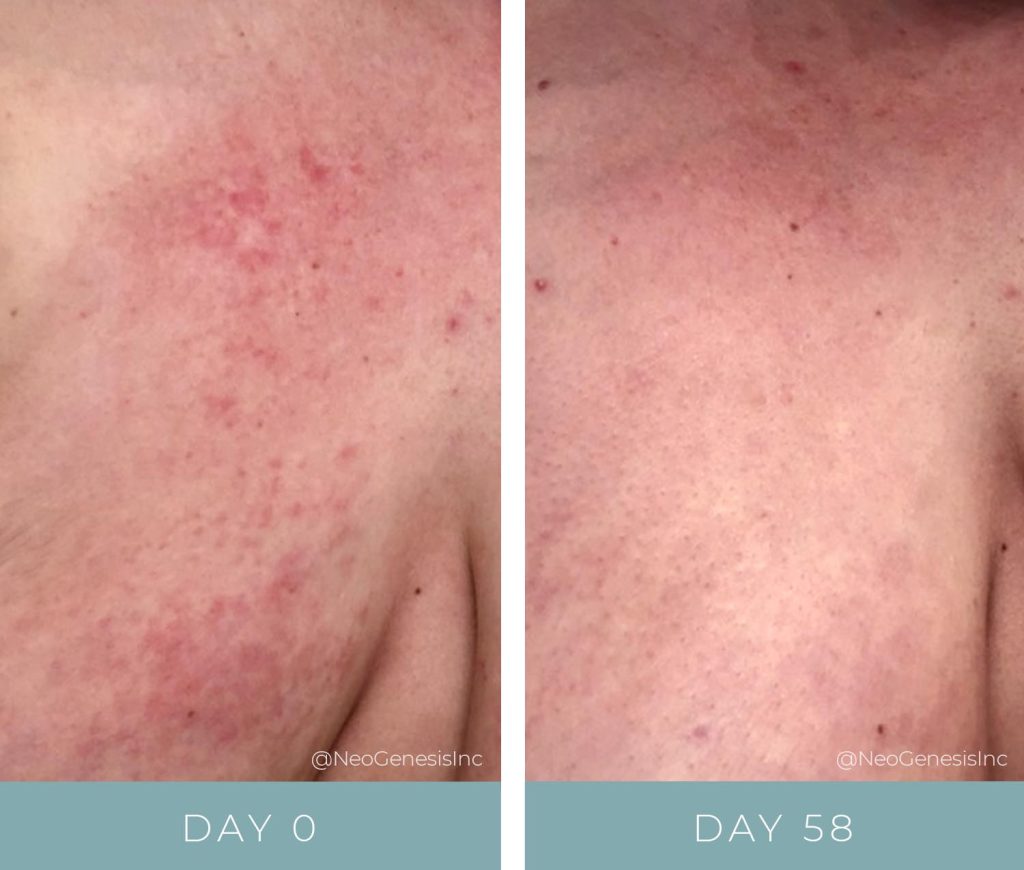
ACTINIC PURPURA
Actinic purpura, also known as solar purpura or senile purpura, is a skin condition that primarily affects older adults. It is characterized by the appearance of purple or red bruises on the arms, hands, and face. These bruises are caused by damage to the blood vessels in the skin due to long-term sun exposure.
The term “actinic” refers to the ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun that cause the skin damage. As we age, our skin becomes thinner and less elastic, making it more susceptible to bruising. In addition, prolonged exposure to UV rays can weaken blood vessel walls, leading to easy bruising.
Actinic purpura is a benign condition and does not pose any serious health risks. The bruises may take weeks to fade away, leaving behind a yellowish or brownish discoloration that can last even longer.
While actinic purpura is more common in older individuals, it can also affect younger people who have had significant sun exposure throughout their lives. People with fair skin and those who live in sunny climates are at a higher risk of developing this condition.
There is no specific treatment for actinic purpura, but there are steps that can be taken to minimize its appearance. These include wearing protective clothing and sunscreen when spending time outdoors, avoiding prolonged sun exposure during peak hours, and using moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and less prone to bruising.